Cloud vs. On-Premise Solutions: What’s Best for Your Business? A Tale of Two Infrastructures
The digital world offers a fascinating dichotomy when it comes to infrastructure: the boundless expanse of the cloud versus the controlled environment of on-premise solutions. Choosing between these two titans can feel like selecting a ship for a perilous voyage – the wrong choice can lead to disaster, while the right one ensures a smooth and prosperous journey. But how do you navigate this complex landscape? This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision that best suits your business’s unique needs and aspirations.
The Cloud: A Sea of Possibilities
Imagine a vast ocean brimming with resources – that’s the cloud. Scalability is its greatest strength. Need more processing power? Just tap into the seemingly endless reserves. Need less? Scale down effortlessly, avoiding wasted resources and unnecessary costs. This elasticity makes the cloud particularly attractive to businesses experiencing rapid growth or facing unpredictable demands. Think of a seasonal retailer – they can surge their capacity during peak periods and gracefully reduce it during the lull.
Furthermore, the cloud offers unparalleled accessibility. Access your data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering collaboration and enabling remote work with ease. This flexibility extends to disaster recovery, as cloud providers often offer redundant systems across multiple geographic locations, minimizing downtime in the event of unforeseen circumstances.
On-Premise: Charting Your Own Course
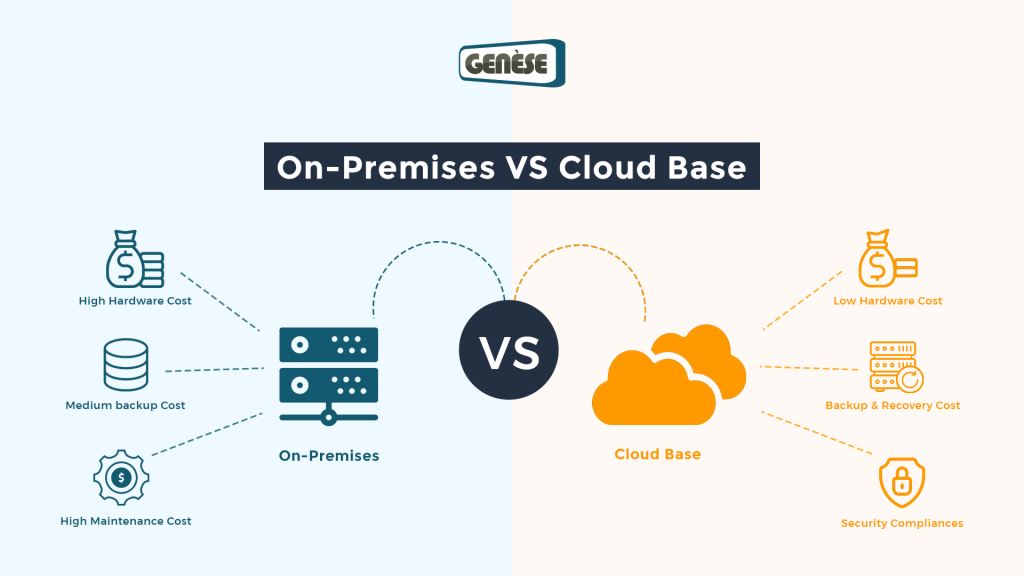
On the other hand, on-premise solutions represent a more traditional approach – owning and managing your own infrastructure. This offers a high degree of control and security. You’re the captain of your ship, responsible for every aspect, from hardware maintenance to security protocols. This level of control can be invaluable for businesses handling highly sensitive data or subject to strict regulatory compliance. The predictability of costs can also be a significant advantage, especially for businesses that prefer a fixed budget approach.
Comparing the Titans: A Head-to-Head
Let’s break down the key differences in a digestible format:
| Feature | Cloud | On-Premise |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go, variable | Upfront investment, fixed costs |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited scalability, requires planning |
| Accessibility | Anywhere with internet connection | Limited to internal network |
| Security | Shared responsibility | Full control, higher responsibility |
| Maintenance | Provider managed | In-house management |
| Control | Limited | Complete |
The Verdict: It Depends
There’s no universally “better” solution. The optimal choice hinges on a multitude of factors, including:
- Budget: Cloud solutions offer flexibility but can become expensive if not managed carefully. On-premise demands a significant upfront investment.
- Security Requirements: Highly sensitive data often necessitates the control afforded by on-premise solutions.
- IT Expertise: On-premise solutions require a dedicated IT team, while cloud solutions lessen this burden.
- Scalability Needs: Rapidly growing businesses will likely benefit from the cloud’s elasticity.
- Compliance Regulations: Certain industries have strict regulations that may necessitate on-premise solutions.
Navigating the Waters: A Strategic Approach
The best approach is often a hybrid model – leveraging the strengths of both cloud and on-premise solutions. Critical applications requiring tight control might reside on-premise, while less sensitive workloads benefit from the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the cloud. This nuanced strategy allows businesses to tailor their infrastructure to their specific needs, maximizing efficiency and minimizing risk.
Choosing between cloud and on-premise is not a simple yes or no answer. It’s a strategic decision that requires careful consideration of your business’s unique requirements and long-term goals. By thoughtfully weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each approach, you can chart a course toward a robust and efficient digital infrastructure that propels your business towards success.

Additional Information
Cloud vs. On-Premise Solutions: Choosing the Right Fit for Your Business
The decision between cloud and on-premise solutions is a critical one for any business, impacting IT infrastructure, budget, security, and scalability. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer; the best choice depends heavily on your specific needs and circumstances. Let’s delve into a detailed comparison:
I. On-Premise Solutions:
-
Definition: On-premise solutions involve hosting your IT infrastructure (servers, databases, applications, etc.) within your own physical location, typically your office building or a data center you own or lease. You are responsible for all aspects of its management.
-
Advantages:
- Greater Control: You have complete control over your data, hardware, and software. This is particularly important for businesses with strict regulatory compliance requirements or sensitive data.
- Enhanced Security (Potentially): With proper security measures in place, on-premise solutions can offer strong security, as you manage all access points and security protocols. However, this requires significant investment in expertise and infrastructure.
- Predictable Costs (Initially): While initial capital expenditure can be high, ongoing operational costs are generally more predictable, excluding maintenance and upgrades.
- Customization: You have maximum flexibility to customize your infrastructure and applications to precisely match your business requirements.
- Offline Capability: Operations are not reliant on internet connectivity. This is crucial for businesses operating in areas with unreliable internet access.
-
Disadvantages:
- High Initial Investment: Significant upfront costs are needed for hardware, software licenses, setup, and IT personnel.
- Ongoing Maintenance Costs: You are responsible for all maintenance, upgrades, repairs, and security patching, leading to potentially high operational costs over time.
- Limited Scalability: Scaling up or down requires significant planning, investment, and potential downtime. Adding capacity can be slow and expensive.
- Expertise Required: You need skilled IT staff to manage and maintain the infrastructure, which can be challenging to find and retain.
- Space Constraints: You need physical space to house the servers and equipment.
- Disaster Recovery: Implementing robust disaster recovery plans requires substantial investment and planning.
II. Cloud Solutions:
-
Definition: Cloud solutions involve hosting your IT infrastructure and applications on servers maintained by a third-party provider (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud). You access these resources over the internet.
-
Advantages:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go models eliminate the need for large upfront investments. You only pay for the resources you consume.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Easily scale resources up or down based on your needs, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. Adding capacity is usually quick and simple.
- Accessibility: Access your data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Reduced Maintenance: The cloud provider handles most of the maintenance, updates, and security patching.
- Automatic Backups and Disaster Recovery: Cloud providers typically offer robust backup and disaster recovery solutions.
- Increased Collaboration: Cloud-based solutions facilitate easier collaboration among employees and external partners.
-
Disadvantages:
- Vendor Lock-in: Migrating from one cloud provider to another can be complex and costly.
- Security Concerns: While cloud providers invest heavily in security, you are reliant on their security measures, and data breaches are still a possibility.
- Internet Dependency: Your operations are entirely dependent on a stable internet connection.
- Limited Control: You have less control over your data and infrastructure compared to on-premise solutions.
- Potential Latency: Depending on your location and the provider’s infrastructure, latency can impact performance.
- Cost Uncertainty: While generally cost-effective, uncontrolled usage can lead to unexpectedly high bills.
III. Hybrid Cloud Approach:
A hybrid cloud approach combines both on-premise and cloud solutions. This offers a balance between control, security, and flexibility. Sensitive data or critical applications can be kept on-premise, while less critical applications or data can be hosted in the cloud.
IV. Factors to Consider When Choosing:
- Budget: Consider initial investment, ongoing operational costs, and potential scalability costs.
- Security Requirements: Assess your data sensitivity and regulatory compliance requirements.
- Scalability Needs: Determine your current and future needs for processing power, storage, and bandwidth.
- IT Expertise: Evaluate your internal IT capabilities and the need for external support.
- Data Location and Compliance: Consider data sovereignty laws and regulations.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: Evaluate the resilience and recovery capabilities of each option.
- Application Requirements: Determine the compatibility of your applications with cloud or on-premise environments.
V. Conclusion:
The optimal choice between cloud and on-premise solutions depends on your specific business requirements, resources, and risk tolerance. Carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each option, considering your long-term goals and the factors listed above. Don’t hesitate to consult with IT professionals to help you make an informed decision that best aligns with your business needs. A hybrid approach might also be the ideal solution for many businesses.