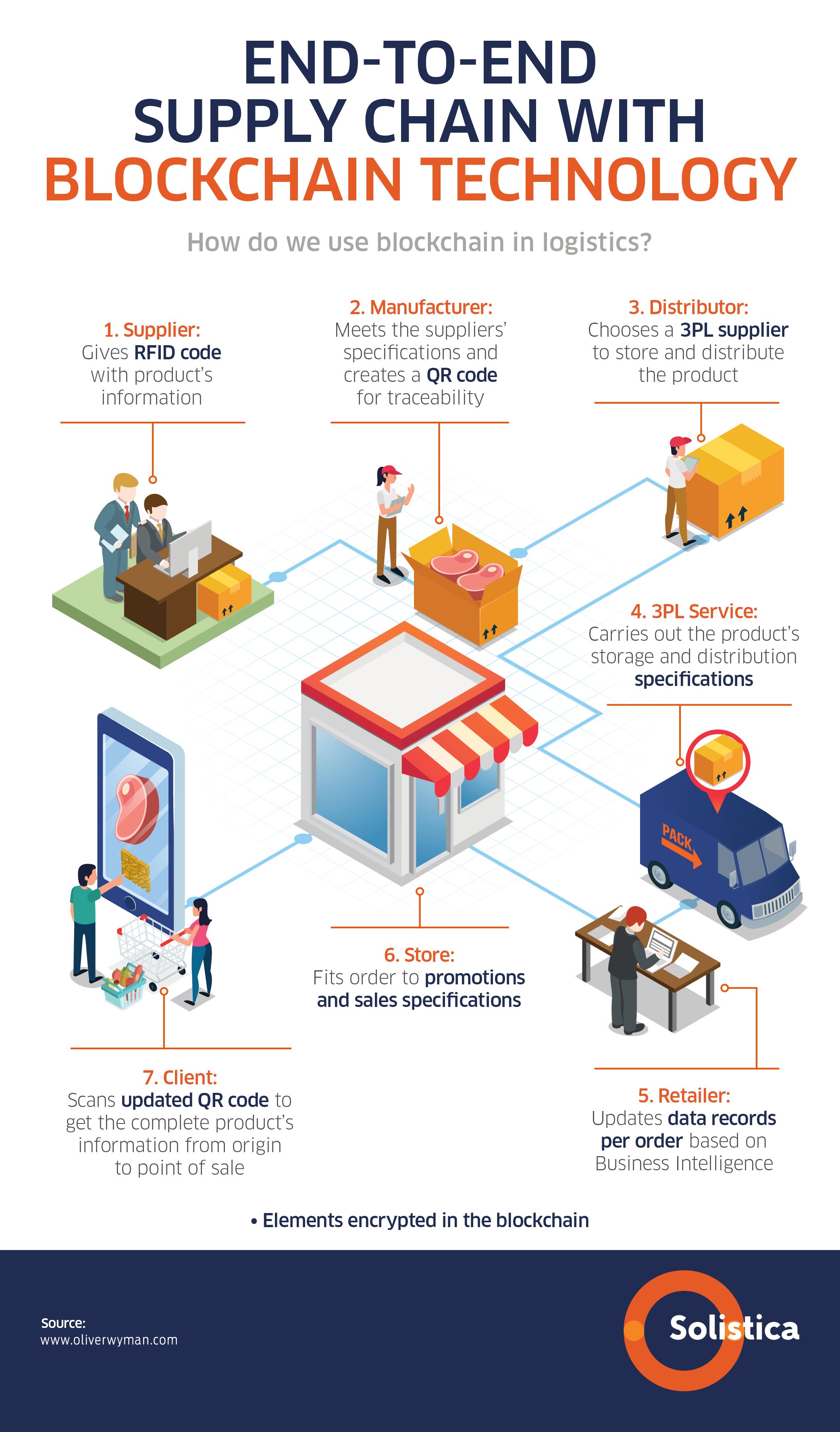
Blockchain: Weaving Trust and Transparency into the Fabric of Supply Chain Management
The global supply chain, a complex tapestry of interconnected businesses, logistics, and transportation, has long struggled with issues of transparency, traceability, and trust. From the origin of raw materials to the delivery of finished goods, information often gets lost in translation, leading to inefficiencies, delays, and even fraud. Enter blockchain technology, a revolutionary force poised to reshape the industry by offering a secure, transparent, and immutable record of every transaction and movement within the supply chain. This isn’t just incremental improvement; it’s a paradigm shift, promising to streamline operations, reduce costs, and build unprecedented levels of confidence among all stakeholders.
Unraveling the Blockchain Advantage:
Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain utilizes a decentralized, distributed ledger. This means that transaction data isn’t stored in a single location, vulnerable to manipulation or hacking. Instead, it’s replicated across a network of computers, making it virtually tamper-proof. This inherent security fosters trust among all parties, from manufacturers and suppliers to distributors and consumers.
Key Transformations Driven by Blockchain:
-
Enhanced Traceability: Blockchain’s granular tracking capabilities allow businesses to pinpoint the exact origin and journey of products. This is particularly crucial in industries like food and pharmaceuticals, where product provenance is paramount for safety and regulatory compliance. Imagine effortlessly tracing a batch of coffee beans from a specific farm in Colombia to your local café, verifying its authenticity and ethical sourcing along the way.
-
Improved Transparency: All participants in the supply chain have access to the same shared, immutable record. This eliminates information asymmetry, promoting collaboration and efficiency. Real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipping schedules, and other critical data points allows for proactive decision-making and minimizes disruptions.
-
Streamlined Processes: Smart contracts, self-executing agreements encoded on the blockchain, automate many manual processes, reducing paperwork, human error, and delays. This can significantly accelerate the flow of goods and reduce operational costs. For instance, automated payments upon delivery eliminate the need for complex invoicing and reconciliation processes.
-
Strengthened Security: The decentralized and cryptographic nature of blockchain makes it exceptionally resilient to fraud and counterfeiting. This is particularly valuable for combating the significant problem of counterfeit goods, protecting brand reputation, and safeguarding consumer safety.
-
Increased Efficiency: By reducing delays, improving communication, and automating processes, blockchain enhances overall supply chain efficiency. This translates to lower costs, faster delivery times, and improved customer satisfaction.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies:
Blockchain is already finding its way into various sectors:
- Pharmaceuticals: Tracking drugs throughout the supply chain ensures authenticity and prevents the distribution of counterfeit medications.
- Food and Agriculture: Verifying the origin and journey of food products enhances food safety and traceability, allowing for rapid responses in case of recalls or contamination.
- Luxury Goods: Combating counterfeiting and ensuring the authenticity of luxury items builds brand trust and protects against revenue loss.
- Retail: Improving supply chain visibility and efficiency enhances inventory management and reduces waste.
Table: Blockchain’s Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Key Benefit | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Enhanced drug traceability and anti-counterfeiting | Tracking medication from manufacturing to patient |
| Food & Beverage | Improved food safety and transparency | Tracing produce from farm to supermarket |
| Luxury Goods | Authentication and anti-counterfeiting | Verifying the authenticity of a designer handbag |
| Retail | Efficient inventory management | Optimizing stock levels and reducing waste |
Challenges and Considerations:
While the potential of blockchain is immense, several challenges remain:
- Scalability: Handling large volumes of data efficiently is crucial for widespread adoption.
- Interoperability: Different blockchain platforms need to communicate seamlessly.
- Regulatory Framework: Clearer regulations are needed to govern the use of blockchain in supply chains.
- Implementation Costs: Implementing blockchain technology can involve significant upfront investment.
The Future of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management:
Despite these challenges, the future of blockchain in supply chain management is bright. As technology matures and adoption increases, we can expect even greater levels of transparency, efficiency, and trust. The potential for improved sustainability, reduced waste, and enhanced ethical sourcing is significant. Blockchain isn’t just a technological innovation; it’s a catalyst for a more responsible and efficient global supply chain, one built on trust and powered by transparency.

Additional Information
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing supply chain management by offering unprecedented transparency, traceability, and efficiency. Its decentralized and immutable nature addresses many long-standing challenges in the industry, including lack of visibility, data inaccuracy, counterfeiting, and inefficient processes. Here’s a detailed analysis of its transformative impact:
1. Enhanced Transparency and Traceability:
- Product Journey Mapping: Blockchain creates a shared, immutable record of a product’s journey from origin to consumer. Each transaction, including sourcing, manufacturing, transportation, and distribution, is recorded on the blockchain, providing complete visibility into the supply chain. This allows businesses to track products in real-time, identify bottlenecks, and respond quickly to disruptions.
- Counterfeit Prevention: The transparent and auditable nature of blockchain makes it extremely difficult to introduce counterfeit products. Each product can be assigned a unique digital identifier linked to its verifiable history on the blockchain, enabling consumers and businesses to authenticate products and verify their authenticity.
- Improved Recall Management: In case of a product recall, blockchain facilitates efficient and precise identification of affected products, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with recalls. The granular level of tracking enables rapid isolation of the affected batch, minimizing disruption.
2. Increased Efficiency and Reduced Costs:
- Streamlined Processes: Automating processes through smart contracts eliminates the need for manual data entry and reconciliation, reducing administrative overhead and improving efficiency. Smart contracts can automatically trigger payments upon delivery, automate quality control checks, and manage logistics.
- Reduced Operational Costs: By improving transparency and traceability, blockchain minimizes inefficiencies and delays. Improved inventory management and reduced waste further contribute to cost savings.
- Faster Transaction Times: Blockchain eliminates intermediaries and streamlines communication between different stakeholders, leading to faster processing of transactions and reduced lead times.
3. Improved Collaboration and Trust:
- Shared Data Platform: Blockchain creates a shared, trusted data platform that all stakeholders can access. This fosters greater collaboration and improves information flow, enhancing decision-making and coordination across the supply chain.
- Enhanced Trust: The immutability of blockchain data builds trust between different parties involved in the supply chain. This transparency reduces disputes and enhances business relationships.
- Data Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic security features protect data from unauthorized access and manipulation, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
4. Specific Applications in Supply Chain Management:
- Food Safety and Traceability: Tracking food products from farm to table ensures food safety and reduces the risk of outbreaks. Blockchain allows for quick identification of contaminated products and their source.
- Pharmaceutical Supply Chain: Tracking pharmaceuticals throughout their lifecycle prevents counterfeiting and ensures product authenticity, improving patient safety.
- Luxury Goods: Verifying the authenticity of luxury items prevents counterfeiting and enhances brand protection.
- Retail: Enhancing transparency and traceability for consumers improves brand loyalty and strengthens customer relationships.
- Logistics and Transportation: Optimizing transportation routes, tracking shipments in real-time, and improving efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations:
- Scalability: Some blockchain networks struggle to handle the large volume of data generated by complex supply chains.
- Interoperability: Different blockchain platforms may not be compatible with each other, hindering seamless data exchange.
- Regulation and Standardization: Lack of clear regulatory frameworks and industry standards can hinder wider adoption.
- Implementation Costs: Implementing blockchain solutions can be costly, requiring significant investment in infrastructure and expertise.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Careful consideration of data privacy and security is crucial to ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Conclusion:
Blockchain technology holds immense potential to transform supply chain management by improving transparency, traceability, efficiency, and collaboration. While challenges remain, ongoing development and wider adoption are paving the way for a more efficient, secure, and resilient supply chain ecosystem. The focus is shifting from proof-of-concept projects to real-world implementations demonstrating significant ROI across various industries. As technology matures and regulatory frameworks evolve, blockchain’s impact on supply chain management will only continue to grow.