What is Cloud Computing and Why It’s Important for Your Business?
The digital landscape is a vast ocean, and businesses are constantly battling waves of data, competition, and ever-evolving technology. Navigating this ocean requires the right tools, and for many businesses, that tool is cloud computing. But what exactly is cloud computing, and why is it so crucial for thriving in today’s market? Let’s dive in.
Decoding the Cloud: More Than Just “Stuff in the Internet”
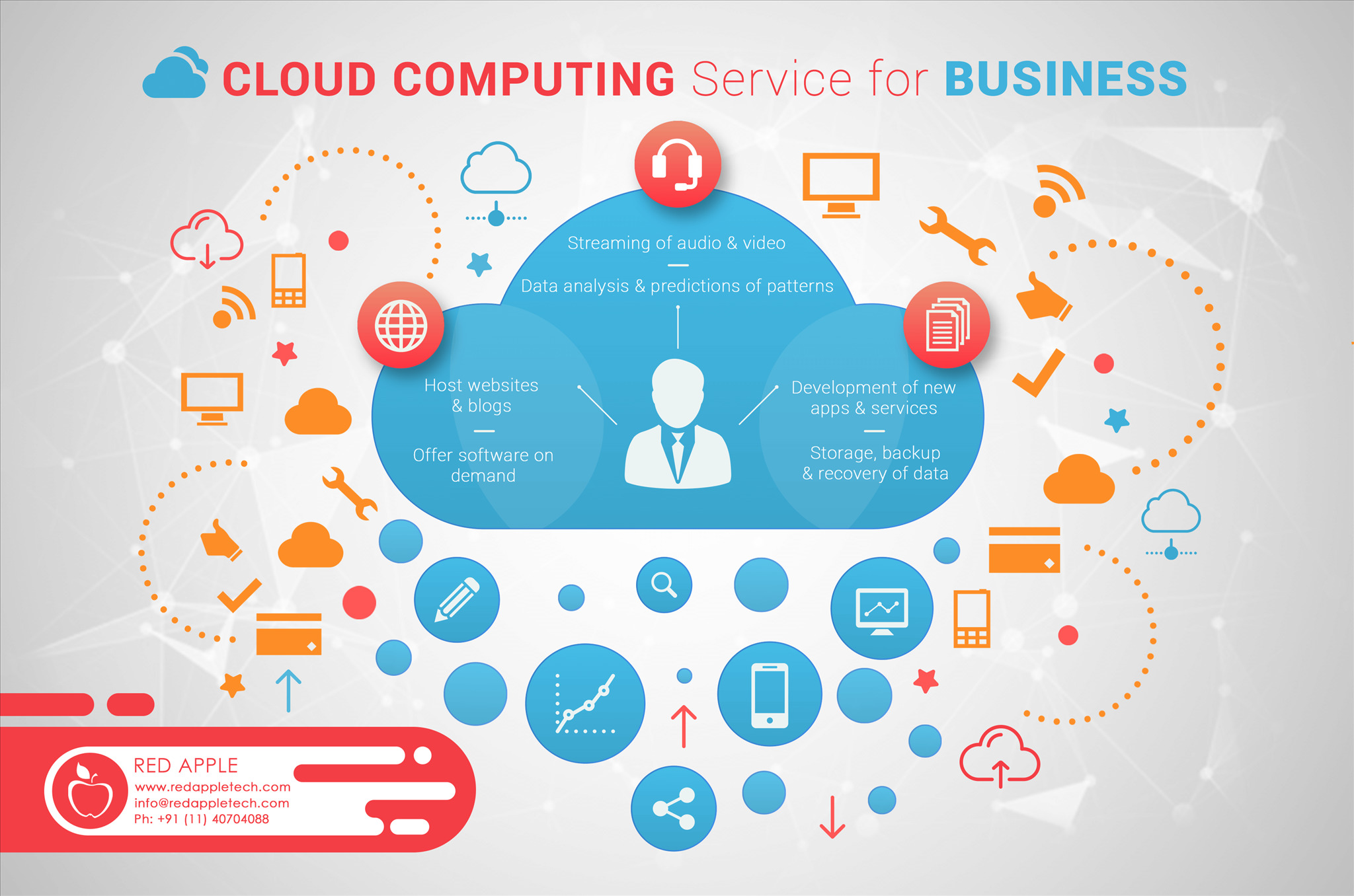
Imagine a vast, powerful utility – like electricity or water – but instead of powering your lights or tap, it powers your entire business infrastructure. That’s the essence of cloud computing. It’s the on-demand availability of computer system resources, everything from servers and storage to databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the internet (“the cloud”). Instead of owning and maintaining these resources in-house, you access them as a service, paying only for what you use.
Think of it like this: you don’t need to own a water treatment plant to have clean water; you simply turn on your tap. Similarly, you don’t need to build and maintain your own data center to benefit from powerful computing resources; you access them through the cloud.
Types of Clouds: Finding the Perfect Fit
The cloud isn’t a monolith. Several service models cater to diverse business needs:
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): The most fundamental level. Think of it as renting the raw materials – servers, storage, networking – to build your own applications and infrastructure. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2 and Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines.
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS): This provides a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications without the hassle of managing the underlying infrastructure. Think of it as renting a pre-built house; you furnish and decorate it, but you don’t worry about the foundation or plumbing. Examples include Google App Engine and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
-
Software as a Service (SaaS): The most user-friendly model. You access software applications over the internet, without needing to install or manage them. Think of it as renting a fully furnished and decorated apartment; you simply move in. Examples include Salesforce, Gmail, and Dropbox.
Why Your Business Needs the Cloud: A Competitive Edge
The advantages of cloud computing are numerous, transforming how businesses operate and compete:
| Benefit | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Reduced IT infrastructure costs, lower energy consumption, and pay-as-you-go pricing. | Eliminating on-site server maintenance costs. |
| Scalability | Easily adjust resources up or down based on demand. | Handling seasonal sales spikes without extra hardware. |
| Accessibility | Access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. | Employees working remotely accessing crucial data. |
| Enhanced Security | Robust security measures provided by cloud providers. | Data encryption and protection against cyber threats. |
| Increased Agility | Faster deployment of new applications and services. | Launching new products to market much quicker. |
| Data Backup & Recovery | Secure, automated backups and easy disaster recovery. | Quick restoration after a data loss event. |
Navigating the Cloud: Choosing the Right Path
Selecting the right cloud strategy isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Consider:
- Your business size and needs: A small startup might benefit from SaaS, while a large enterprise might require IaaS for greater control.
- Your budget: Cloud pricing models vary; careful planning is essential.
- Your technical expertise: Some cloud services require more technical expertise than others.
- Security and compliance requirements: Choose a provider that meets your industry’s regulations.
The Cloud: A Future-Proofing Strategy
Cloud computing is more than a trend; it’s a foundational shift in how businesses operate. By embracing the cloud, you’re not just adopting a technology; you’re adopting a strategy for growth, agility, and resilience in a rapidly evolving digital world. It’s the key to unlocking new opportunities and staying ahead of the competition. The future of business is in the cloud, and the time to embrace it is now.
Additional Information
Cloud Computing: A Deep Dive and its Business Importance
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage (cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Instead of owning and maintaining physical data centers and servers, businesses access these resources over the internet from a cloud provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), etc.
Key Components of Cloud Computing:
- On-demand self-service: Users can provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
- Broad network access: Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations).
- Resource pooling: The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand. This means resources are shared, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings.
- Rapid elasticity: Capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released, in some cases automatically, to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand. To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be appropriated in any quantity at any time.
- Measured service: Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g., storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts). Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for both the provider and consumer of the utilized service.
Types of Cloud Services:
Cloud computing is typically categorized into three main service models:
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides fundamental computing resources like virtual machines, storage, and networking. You manage the operating systems, applications, and data. Examples include AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine. This offers the most control but also the most responsibility.
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Provides a platform for developing, running, and managing applications without the complexity of managing the underlying infrastructure. You manage the applications and data, but the provider handles the servers, operating systems, and middleware. Examples include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure App Service, and Google App Engine. This offers a good balance between control and ease of use.
-
Software as a Service (SaaS): Provides ready-to-use software applications accessed over the internet. You don’t manage anything; the provider handles everything. Examples include Salesforce, Microsoft 365, and Google Workspace. This is the easiest to use but offers the least control.
Why Cloud Computing is Important for Your Business:
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages for businesses of all sizes:
- Cost Savings: Reduced capital expenditure on hardware, software, and IT infrastructure. Pay-as-you-go models significantly lower upfront investment.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance without overspending on idle capacity.
- Increased Efficiency: Automate tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives. Improved collaboration and productivity through readily available resources and tools.
- Enhanced Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, often exceeding the capabilities of individual businesses.
- Improved Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud services offer robust data backup and recovery mechanisms, minimizing downtime in case of unforeseen events.
- Accessibility and Collaboration: Access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating remote work and collaboration.
- Innovation and Agility: Focus on core business functions, leveraging cloud-based tools and services to accelerate innovation and time to market.
- Competitive Advantage: Access advanced technologies and analytics capabilities previously unavailable to smaller businesses.
Challenges of Cloud Computing:
- Security Concerns: Data breaches and security vulnerabilities remain a concern, requiring careful selection of providers and implementation of robust security measures.
- Vendor Lock-in: Migrating from one cloud provider to another can be complex and costly.
- Internet Dependency: Cloud services rely on internet connectivity; outages can disrupt operations.
- Compliance Requirements: Businesses must ensure their cloud deployments comply with relevant regulations and industry standards.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating cloud services with existing on-premise systems can be challenging.
In conclusion, cloud computing offers a powerful and transformative technology that can significantly benefit businesses. However, careful planning, due diligence, and a clear understanding of your business needs are crucial for successful cloud adoption. Evaluating the different cloud models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and choosing the right provider are key steps in maximizing the benefits and mitigating the risks associated with cloud computing.